Lithium Crash Foretold: BYD's Chile Fiasco Sparks Warnings for the Future
Due to a significant decline in global lithium prices, BYD has abandoned its plan to construct a lithium iron phosphate (LFP) cathode plant in Chile. This change impacts the venture’s financial viability. As one of the largest producers globally, Chile was set to host this multimillion-dollar initiative involving both BYD and Tsingshan Group.
Reuters Reports indicate that Chile’s National Economic Development Agency (Corfo) verified that both BYD and Tsingshan have withdrawn their investments because of the significant drop in lithium prices. Tsingshan ceased a $233 million initiative intended to yield an annual production of 120,000 tons of LFP, whereas BYD, which was considering investing $290 million in constructing a facility with a capacity of 50,000 tons per year for LFP cathodes, informed authorities about its decision to pull out back in January.
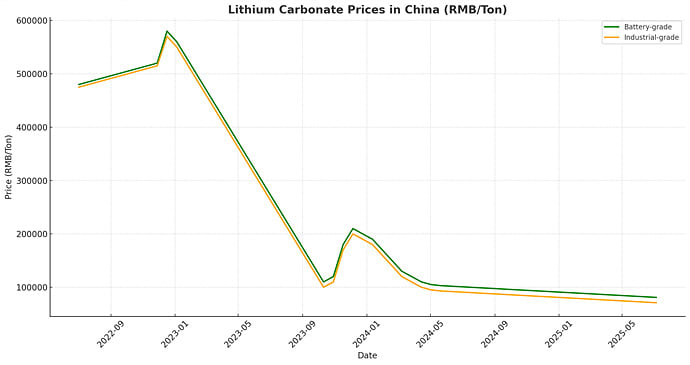
The cost of lithium carbonate surged due to the rise of electric vehicles, reaching an apex of 590,000 CNY (approximately 81,500 USD) per ton in November 2022. However, these prices have dropped significantly beneath 70,000 CNY (around 9,700 USD) per ton since then. Given their crucial role as primary constituents in LFP batteries, fluctuations in both lithium carbonate and iron phosphate pricing substantially affect financial choices within this industry.
Even though BYD obtained lithium mining rights from the Chilean government in January 2022 and secured a primary supply agreement for lithium carbonate in April 2023, they have reconsidered their production plant strategies because of the plummeting prices.
The shift in BYD’s investments underscores how fluctuations in resource prices can affect supply chain approaches, indicating potential hurdles for Chinese battery makers looking to expand internationally.
BYD’s strategy to establish an end-to-end supply chain in Chile, covering everything from raw materials to battery manufacturing, appears to have encountered obstacles due to the plummeting prices of lithium. It might be more economical for the firm to leverage its current operations in China instead. This change underscores the importance for manufacturers of batteries to lessen their dependence on external sources and develop adaptable sourcing approaches.
Should lithium prices steady and recover, both BYD and its rivals might reassess their investment plans for countries abundant in lithium such as Chile or Argentina. In the short term, they probably will concentrate more on optimizing current processing capacities instead of undertaking expensive endeavors focused on mining to battery production chains.
BYD might have to revise its export approach for budget-friendly LFP variants. Difficulties in obtaining cost-effective raw materials could impact the competitive pricing of its electric cars in international markets.
[CryptoTrendLens.blogspot.com] Newest posts!
・ Renault's $179K R5 Turbo 3E Is Adorably Styled but Handles Like a Supercar
・ Will Central Park Soon Prohibit Electric Bicycles? Implications for New York’s Future
・ The Upcoming Era of Automobiles: How Software Has Become the Core of Car Innovations
Posting Komentar untuk "Lithium Crash Foretold: BYD's Chile Fiasco Sparks Warnings for the Future"